Recent Archaeological Discoveries 2024
Most Recent Archaeological Discoveries
1. Ancient Urban Settlements Discovered in the Amazon Rainforest
2015 – Ecuador’s National Institute of Cultural Heritage
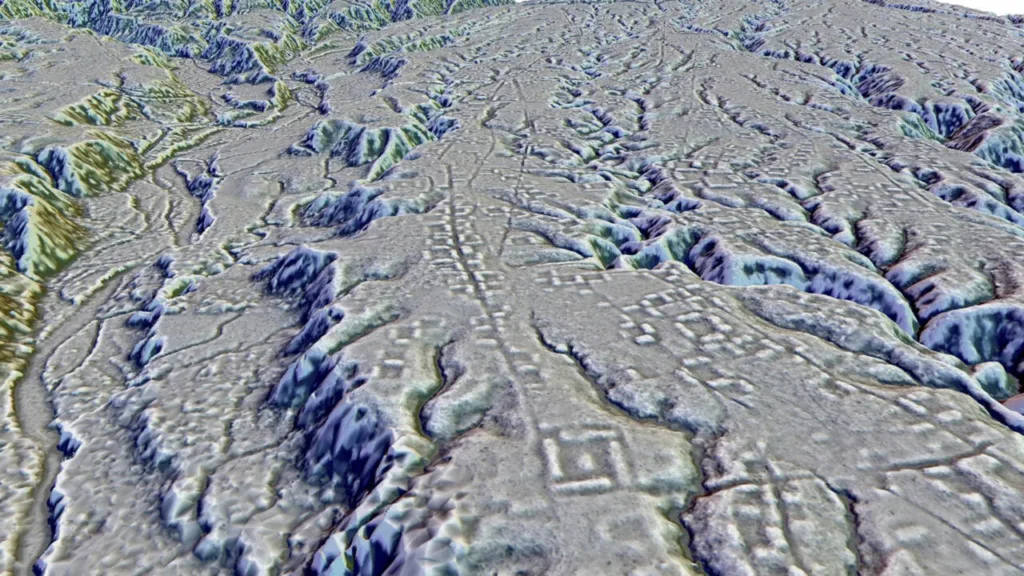
Using LIDAR technology, archaeologists in the Upano Valley in Ecuador have discovered a miracle. They have found evidence of many settlements connected to each other 2,500 years ago. This is important evidence that there was urbanization in the Amazon.
In 2015, Ecuador’s National Institute of Cultural Heritage commissioned a LIDAR scan to conduct research, and they found settlements hidden under the trees. Until now, we believed that humans lived very little in the Amazon in ancient times. But, this discovery has changed that belief. (Ref)
2024 – Research led by Stephane Rostain (French National Research Institute CNRS)
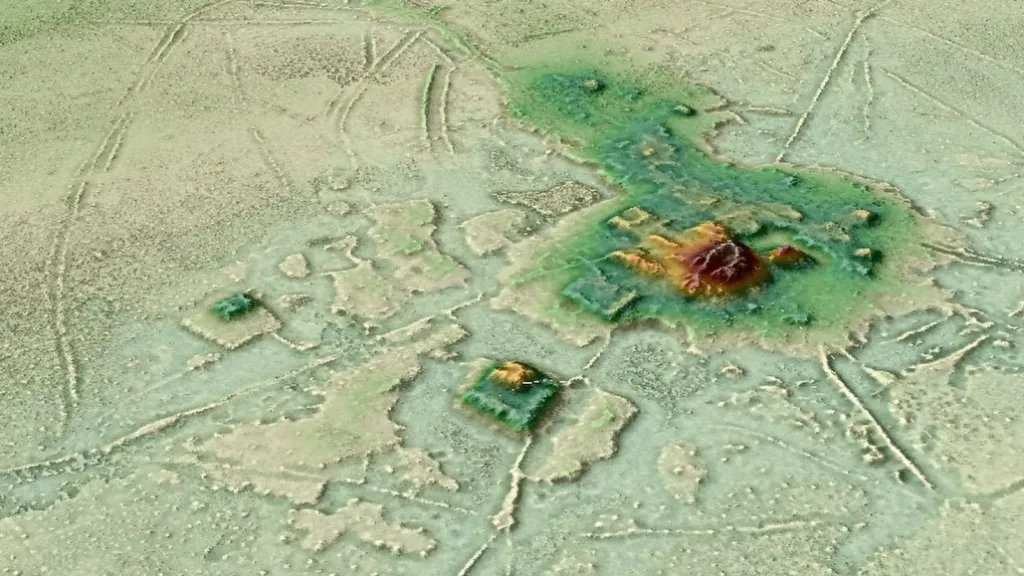
Based on the LIDAR image, a research led by Stephane Rostain of the French National Research Institute CNRS, they have found large community settlements like Sanghe and Kilamob. There are rows of terraces, pottery, and ceremonial structures. The radiocarbon dating has shown that the settlements in the Upano area date from 500 BC to 600 AD. This is 1,000 years older than any other Amazon settlement.
Also, the LIDAR has shown how all the settlements were connected to each other. There were 5 large settlements and 10 small settlements in an area of 300 square kilometers. There was everything there: urbanization, agricultural lands, roads. Also, archaeologists have found many religious buildings and houses at each site. They built cities in a rectangular shape, leveling the mountain tops.
Actually, the Amazon people have never been considered in discussions about civilization by experts. But, this evidence has changed the belief that “The Amazon farmers did not build roads, canals, and large buildings”.
2022 – LIDAR Survey in the Bolivian Amazon
Not only that, a 2022 LIDAR survey of the Bolivian Amazon also found a large urban civilization spanning 4,500 square kilometers. This civilization is known as the Casarabe culture (Llanos de Mojos). Researchers assume this civilization might existed between 500 – 1400 AD. (Ref1, Ref2)

Most Recent Archaeological Discoveries
2. The world’s oldest cave painting has been discovered in Indonesia!
The world’s oldest cave painting has been discovered on the island of Sulawesi in Indonesia. Found in caves inside Mount Karambuwang, this painting shows a wild boar and three human figures. So, it proves that humans were creative in ancient times, and also had the ability to tell stories. This painting is at least 51,200 years old. This is 5,000 years older than the oldest cave painting discovered before this one. The Archaeological discoveries that changed history.

2024 – Discovery and Research Led by Ati Agus Oktaviana
The research team, led by Indonesian rock art expert Ati Agus Octaviana, says that this discovery shows that storytelling was an important cultural feature in ancient Indonesia. In the painting, the story of a pig is illustrated, showing the pig with its mouth open and three human figures seemingly engaged in some activity. It appears to be telling a story.
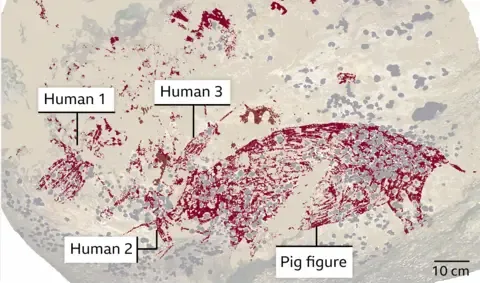
We used to believe that cave paintings were first discovered in Europe. However, this discovery changes that belief, and shows that storytelling played an important role in the art of painting. Also, simple paintings found in South Africa, and the oldest painting discovered in Borneo, all show that people started drawing much earlier than we thought. (Ref)
Scientists are now using a new method to accurately date cave paintings using laser technology, and this technology will pave the way for many more discoveries. With this, we can know more precisely when humans first developed a sense of art. (Ref)
Recent Archaeological Discoveries 2024
3. 3,200-Year-Old Jars Discovered in the Mediterranean!
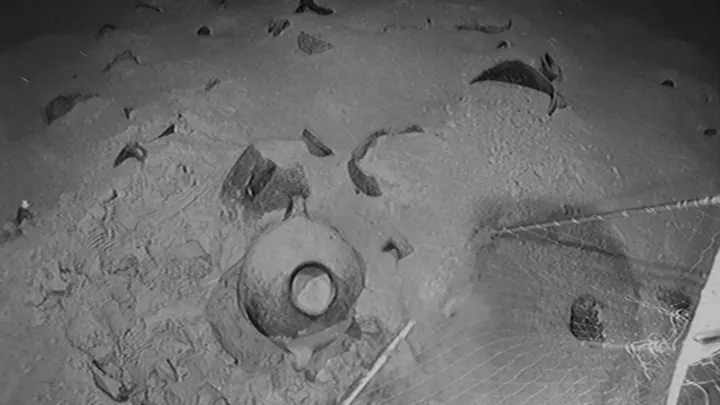
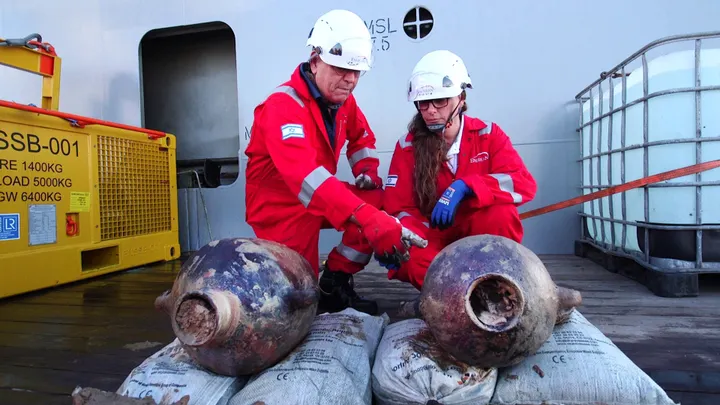
In 2024, two ancient jars were discovered in the Mediterranean Sea. The jars were covered in thick brown clay, about a mile deep in the seabed and 60 miles from shore, where they had been under the sea for more than 3,200 years. It took three hours to bring them to the surface. (Ref)
This is the first discovery of a Bronze Age shipwreck off the coast of Israel. In May, archaeologists recovered these Canaanite storage jars from the sea off northern Israel. Actually, they were part of a large cargo ship.

Historical Context and Significance
Jacob Sharvit, head of the Marine Archaeology Department at the Israel Antiquities Authority (IAA), says the shipwreck is very important because Bronze Age shipwrecks are usually found in shallow water but, this one was found so deep in the sea. Therefore, the recovery of these jars safely was a very challenging task for the IAA and a gas company called Energean. (Ref)
Canaanite jars, which were used for trade in the Mediterranean around 2000 BC, were designed to be stable on ships. The bottoms of the jars were either pointed or rounded, which helped the jars to stay upright on the ship, says expert Shelly Waxman. The jars date back to 1400 to 1200 BC.

“The Mediterranean was an important trading center at that time. There was trade, diplomacy, and communication between many civilizations,” says archaeologist Eric Klein, author of the book “1177 BC: The Year Civilization Fell.”
During that period, great empires like the Egyptians and Hittites controlled trade and diplomacy through the Mediterranean. Merchant ships traveled between Greece, Cyprus, Anatolia, the Levant, and Egypt. Like the Uluburu shipwreck, this discovery shows how closely connected the ancient Mediterranean world was.
Recent Archaeological Discoveries 2024
4. Mysterious Underground Tunnels in Saudi Arabia Reveal 7,000-Year-Old Human Settlements!
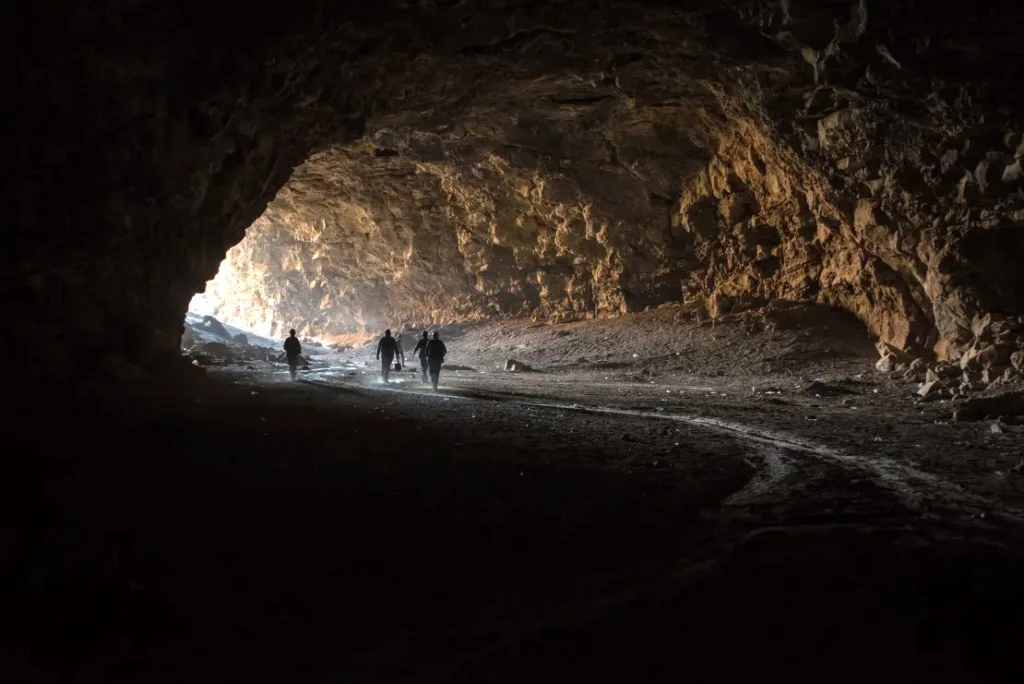

In 2024, the Umm Jirsan lava tube system in Saudi Arabia was opened to explore the mysterious underground tunnels carved by ancient lava flows. The tunnels, which span about 5,000 feet, are in Harrat Khaybar, a gigantic volcanic field that last erupted in the seventh century.
Recent research has revealed that, about 7,000 years ago, humans and animals lived in these caves during the Neolithic and Bronze Age periods. Despite the harsh desert climate of northern Saudi Arabia, which made it difficult for ancient remains to survive, the cool, protected tunnels of Umm Jirsan acted as a natural time capsule, preserving traces of their lives. (Ref)
The research was led by researchers from Griffith University’s Australian Research Center for Human Evolution (ARCHE), in partnership with international collaborators & Saudi Arabian organizations.
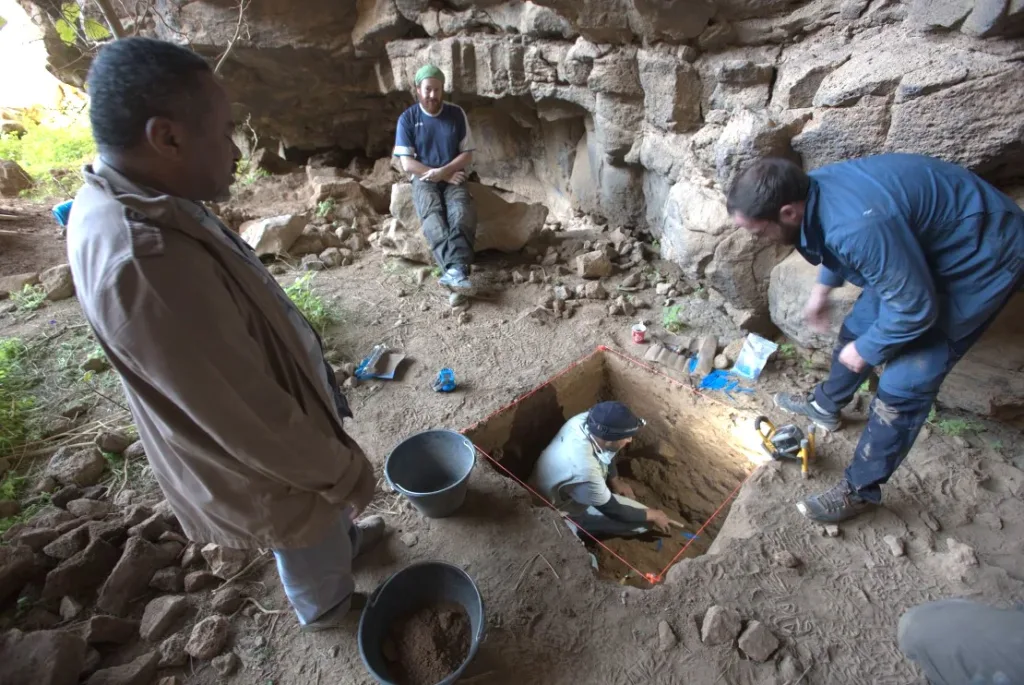

Finally, they found human bones, animal fossils, stone tools, and captivating rock art displaying ancient life. The research continues to find what these ancient people ate and how they farmed. (Ref)
Researcher Matthew Stewart (ARCHE) said, “This is the first clear evidence that people had lived in these caves. This site likely served as an important route to grazing lands, connecting key oases and facilitating cultural exchange and trade”. Like Umm Jirsan, there are thousands of volcanic caves throughout Saudi Arabia, and there are many more amazing discoveries to be made.
Most Recent Archaeological Discoveries
5. Ancient carvings next to dinosaur footprints in Brazil!
Interest in dinosaurs is not new, and our ancestors were also fascinated by these prehistoric creatures. In the city of Paraíba, Brazil, archaeologists have found carvings next to dinosaur footprints that are about 100 million years old.
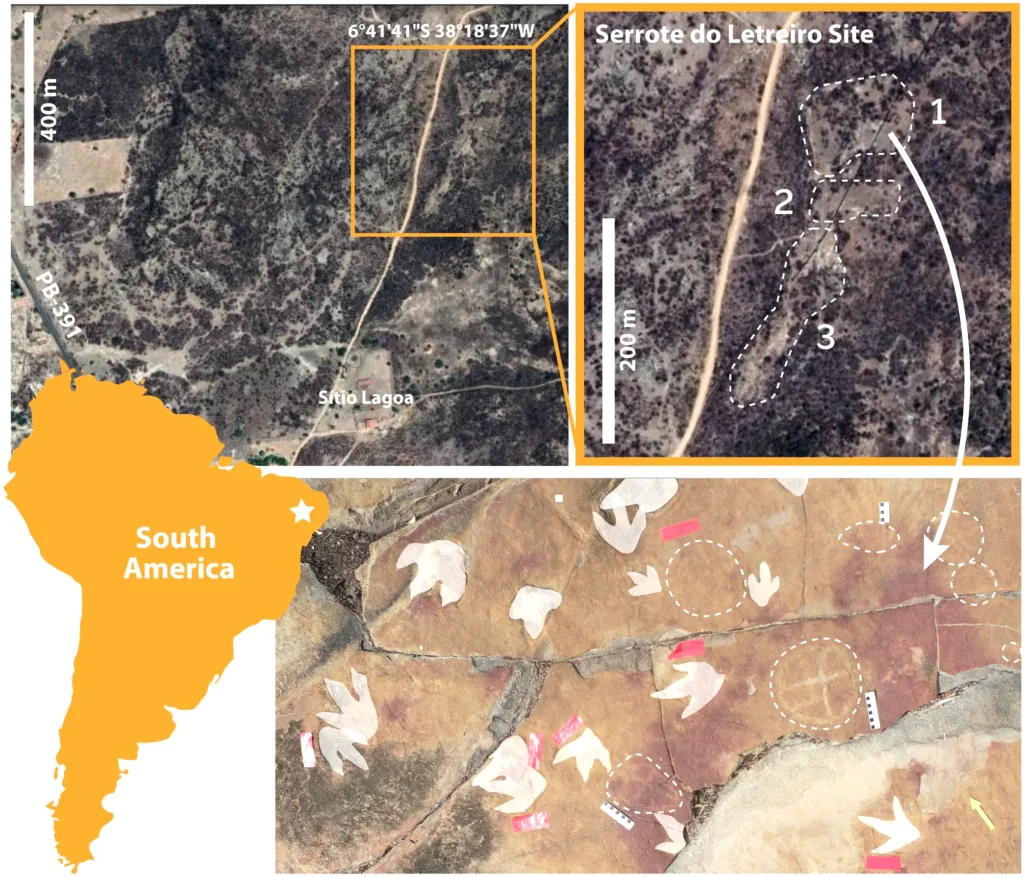
There are no carvings on the dinosaur footprints which means people left the footprints untouched. It is not known why they did this. But, researchers assume that the ancient people who lived in Brazil also respected dinosaurs like we do.
2024 – Scientific Study Published in Scientific Reports
Researchers Troiano, Dos Santos, Aureliano, and Gilardi have published a research paper in Scientific Reports and they pointed out that the carvings did not harm the dinosaur footprints. They also found footprints of similar carvings between 2,620 and 9,400 years old at the same place. (Ref)
There is a place called Cerro do Letreiro in Velasco dos Dinosauros. That is where these carvings exist alongside the footprints of many dinosaurs, including meat-eating theropods and long-necked sauropods.
Even if the carvers did not know anything about dinosaurs, they might have thought that if they were not the footprints of a large flightless bird (rhea), then they were the footprints of an animal called Nodiomastodon flatensis, a relative of modern elephants.
Dinosaur footprints are found in many places around the world, alongside rock carvings. But nowhere have they been seen so closely as in Serrote do Letreiro. This study shows that there is a symbolic connection between human art and ancient fossils.
